Inflammation is the enemy when managing lipedema. This chronic condition—marked by painful fat accumulation in the legs, hips, arms, and other areas—affects millions of women worldwide and often goes undiagnosed or misdiagnosed for years. At Lipedema Surgical Solutions, Dr. Thomas Wright and his team are always looking for ways to help patients manage their symptoms holistically. While surgery can be life-changing, diet and lifestyle choices also play a critical role in managing lipedema.
Emerging research from the University of California (UC) Riverside and UC Davis points to a surprising dietary culprit that may be worsening inflammation—not just in the gut, but potentially in the body systems that affect lipedema: soybean oil.
Soybean oil is one of the most widely consumed cooking oils in the United States. Found in everything from salad dressings and snack foods to fast food fryers and pre-packaged baked goods, soybean oil has become an invisible staple of the American diet. But is it doing more harm than good?
Let’s explore what the latest research says and what this could mean for women living with lipedema.
A Gut Feeling: Why Gut Health Matters in Lipedema
There’s a growing body of evidence showing a strong connection between gut health and systemic inflammation. When your gut microbiome (the trillions of bacteria that live in your digestive tract) is thrown off balance, it can lead to a range of inflammatory issues throughout the body—and that includes worsening lipedema symptoms.
A high-fat, high-calorie diet packed with processed foods has been shown to disrupt the gut microbiota. This is especially important for those with lipedema, as inflammation is not just a symptom of the disease—it can also trigger progression and flare-ups.
The Soybean Oil Problem: What the Studies Say
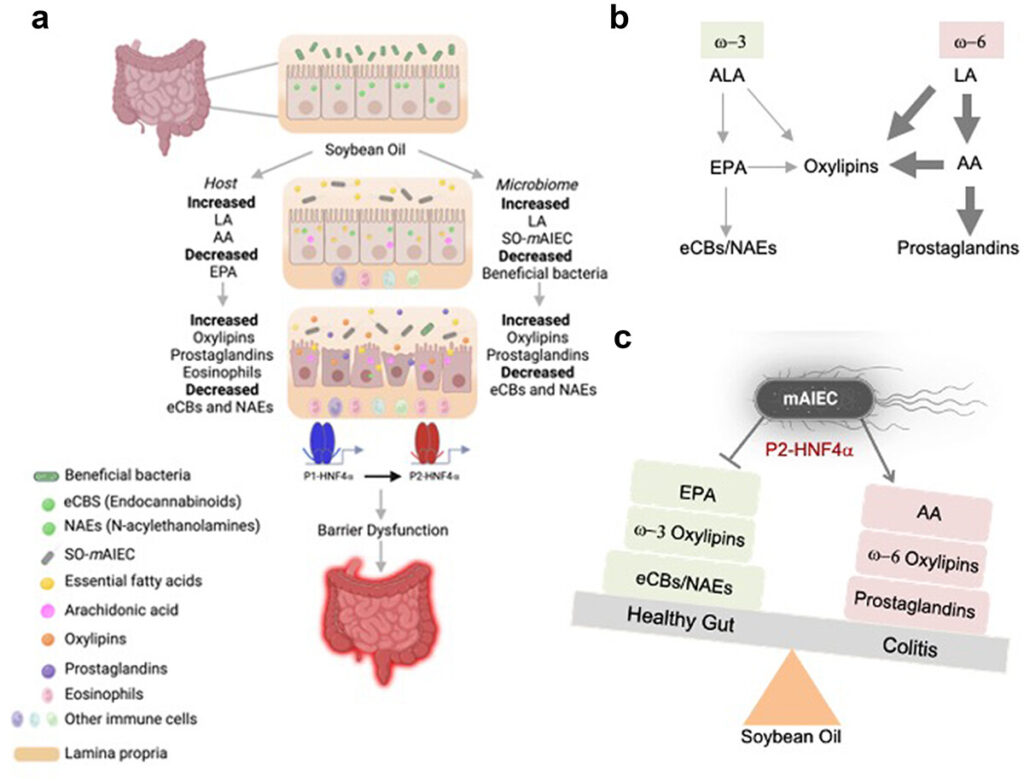
In a recent mouse study conducted by UC Riverside and UC Davis, researchers looked closely at the effects of a diet high in soybean oil, which is rich in linoleic acid, a type of omega-6 fatty acid. While the body needs small amounts of linoleic acid to maintain hydration and cell integrity, too much of it can tip the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory processes.
Here’s what they found:
- Mice on a soybean oil-heavy diet had disrupted gut microbiomes, with a rise in inflammatory bacteria and a decrease in beneficial strains like lactobacillus.
- The mice also had lower levels of endocannabinoids, natural lipid-based molecules that help block inflammation and regulate gut health.
- A leaky gut developed, caused by damage to a key protein (HNF-4α) that maintains the intestinal lining. This allowed toxins and inflammatory agents to enter the bloodstream, worsening systemic inflammation.
- Researchers also found increased levels of oxylipins, inflammatory compounds that have been associated with both obesity and colitis.
The takeaway? A high-linoleic acid diet (like one rich in soybean oil) disrupts the body’s natural anti-inflammatory systems, making it easier for inflammation to spread and persist.
Why This Matters for Women with Lipedema
Lipedema is already marked by abnormal fat accumulation, chronic pain, swelling, and reduced mobility—all of which are exacerbated by inflammation. For patients with lipedema, even small dietary changes that reduce inflammation can significantly impact pain levels, energy, and day-to-day comfort.
When linoleic acid is consumed in excess, it crowds out the enzymes that normally convert omega-3 fatty acids (from flaxseeds, walnuts, and fish oils) into beneficial endocannabinoids. These endocannabinoids help manage pain and inflammation. For women with lipedema, losing this natural regulation system may worsen their symptoms or increase their frequency.
Moreover, research on the endocannabinoid system (ECS) is still in its early stages, but findings so far suggest that it plays a role in visceral pain, fat metabolism, and immune function—all of which are relevant to lipedema.
Soybean Oil and the Rise of Chronic Inflammation in the American Diet
To understand the scale of the issue, consider this: the average American now consumes up to 10% of their daily calories from linoleic acid, which is five to ten times the recommended amount. This drastic increase has happened alongside a massive rise in chronic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, and autoimmune disorders.
For women with lipedema, who may already struggle with metabolic imbalance, this excess may represent a perfect storm that fuels disease progression and hinders symptom management.
Could Cutting Soybean Oil Help Reduce Lipedema Symptoms?
While clinical studies are still needed to confirm a direct link between soybean oil and worsening lipedema, there is enough evidence to warrant caution. At Lipedema Surgical Solutions, we encourage patients to adopt an anti-inflammatory lifestyle, and that includes looking carefully at dietary fats.

Here are some practical ways to reduce linoleic acid and pro-inflammatory oils in your diet:
- Read ingredient labels carefully. Soybean oil goes by many names, including “vegetable oil,” and is often found in processed snacks, breads, sauces, and condiments.
- Cook at home using healthier fats. Opt for olive oil, avocado oil, or coconut oil when cooking.
- Increase omega-3 intake. Include more flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and fatty fish in your meals to help balance the omega-6 to omega-3 ratio.
- Avoid deep-fried or fast foods. These are often cooked in high-linoleic acid oils and may carry hidden sources of inflammation.
- Try fermented foods and probiotics. These help restore gut health and may combat some of the negative effects of processed oils.
What About Endocannabinoid Therapy?
Researchers are now exploring whether restoring endocannabinoid levels could be used as a therapy for inflammatory diseases, including IBD. For lipedema patients, this could open the door to new treatments aimed at improving pain and inflammation through ECS modulation.
That said, dietary changes remain the first and most accessible step for most patients. Supporting the ECS through a high-omega-3, low-linoleic-acid diet may naturally help restore balance and reduce discomfort.
Final Thoughts: Empowering Lipedema Patients Through Nutrition
At Lipedema Surgical Solutions, we believe that managing lipedema requires a 360-degree approach. Surgery can remove diseased fat and improve mobility, but day-to-day symptom control often comes down to the choices you make at the table.
Emerging science around soybean oil, linoleic acid, and the gut-endocannabinoid connection suggests that small changes in diet could lead to big improvements in inflammation management. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms, the initial findings are promising—and empowering.
If you’re living with lipedema and looking to take more control of your health, consider evaluating the oils and fats in your diet. Swap out inflammatory options like soybean oil in favor of nourishing, healing fats. Your gut, your ECS, and your whole body will thank you.
Interested in learning more about holistic approaches to lipedema care or exploring whether lipedema reduction surgery is right for you? Contact Dr. Thomas Wright and the team at Lipedema Surgical Solutions today.
Serving St. Louis, O’Fallon, and surrounding areas
(636) 397-4012
www.lipedema.net